Memory plays a critical role in hardware, enabling the storage and retrieval of data and instructions. From small embedded devices to powerful servers, memory is essential for program execution, multitasking, system performance, and data integrity. Its capacity, speed, and reliability significantly impact computing systems’ functionality and efficiency. This article will explore the importance of memory in hardware and why it is a crucial component in any computing system.
What is flash memory?
Flash memory is a nonvolatile computer storage medium that can retain data even when the power is turned off. It is a high-speed, electrically programmable memory that erases data in units called blocks and rewrites data at the byte level. It is commonly used in electronic devices such as USB drives, solid-state drives (SSDs), memory cards, and smartphones.
Flash memory represents a rewritable storage chip based on electrically erasable programmable read-only memory (EEPROM).
Flash memory works by storing data in memory cells made of floating-gate transistors. These transistors can hold an electric charge, representing either a binary 0 or 1. When a voltage is applied to a memory cell, the charge is trapped in the floating gate, and this charge determines the stored data.
Flash memory is known for its speed and durability. It allows for fast read and write operations, making it suitable for applications that require quick data access. Additionally, flash memory resists mechanical shocks, operates silently, and consumes less power than traditional hard disk drives.
There are two main types of flash memory: NOR flash and NAND flash. NOR Flash allows for random access, meaning individual bytes of data can be directly accessed and modified. It is commonly used in devices where low-density storage and fast random access are essential, such as microcontrollers and firmware storage.
On the other hand, NAND flash is the more common type of flash memory. It offers higher storage capacity and faster read/write speeds than NOR Flash but doesn’t provide random access. NAND flash memory is organized in memory cells grouped into pages, which are further grouped into blocks. To modify data, entire blocks need to be erased and rewritten, which makes it slower for random access but more efficient for large-scale storage applications.
What is NAND flash memory?
NAND flash memory, or “memory chip,” represents high storage capacity and fast read/write speeds technology that does not use power to retain data. An example of NAND flash memory is a microSD card, which mobile phone users can use to store photos, videos, and music.
NAND flash memory possesses several unique characteristics that distinguish it from other storage technologies:
- High Storage Capacity: NAND flash memory offers high-density storage, allowing more significant amounts of data to be stored compactly. This makes it well-suited for applications that require substantial storage capacity, such as SSDs used in laptops and data centers.
- Fast Read/Write Speeds: NAND flash memory enables fast data access with high read and write speeds. This attribute benefits applications requiring quick data retrieval and storage, improving overall system performance.
- Sequential Access: Unlike NOR flash, which allows random access to individual memory cells, NAND flash memory supports sequential access. It reads and writes data in blocks, making it more efficient for large-scale data storage and retrieval operations.
- Cost-Effective: NAND flash memory has become increasingly cost-effective, enabling its widespread adoption in consumer electronics. Advances in manufacturing technology have led to higher production volumes and lower per-unit costs, making NAND flash a popular choice for various devices, including smartphones, tablets, and USB drives.
- Durability and Reliability: NAND flash memory is designed to withstand frequent read and write operations, making it highly durable. It is also resistant to mechanical shock, making it suitable for portable devices that may experience physical impacts.
- Low Power Consumption: NAND flash memory consumes significantly less power than traditional storage options like hard disk drives (HDDs). This energy efficiency is advantageous for battery-powered devices as it helps to extend battery life.
- Wear Leveling and Error Correction: NAND flash memory incorporates wear-leveling algorithms and error correction mechanisms to enhance the lifespan and maintain data integrity. Wear leveling evenly distributes write operations across memory cells, preventing premature wear on specific areas. Error correction techniques help to identify and correct data errors that may occur during storage or retrieval.
NAND flash memory is a nonvolatile storage technology that does not require power to retain data. Its primary goal has been to reduce cost per bit and increase chip capacity, enabling it to compete with magnetic storage devices like hard drives. NAND flash is commonly used in devices with large files, such as MP3 players, digital cameras, and USB flash drives, which are frequently uploaded and replaced.
NAND flash memory stores data in blocks using electric circuits. When power is disconnected, a metal-oxide-semiconductor charges the memory cell, preserving the data. Floating gate transistors (FGTs) are typically used as the metal-oxide-semiconductor. These FGTs are organized in a NAND logic gate structure.
NAND memory cells have two types of gates: control gates and floating gates. These gates control the flow of data. A voltage charge is sent to the control gate to program a cell.
Leading vendors in NAND flash memory include Samsung, Toshiba, Intel, Western Digital, and Micron Technology.
NAND flash memory has a limited number of writing cycles. Failure in NAND flash is usually gradual, as individual cells fail and overall performance degrades, known as wear-out. To mitigate this, some vendors overprovision their systems by adding more memory than claimed.
When a NAND card wears out, the user purchases a new one, and the device continues functioning. By shifting the cost of additional storage to the consumer, manufacturers have significantly lowered the price of consumer electronic devices. Advances in NAND flash memory technology have made the chips smaller, increasing the complete read-write cycles and reducing voltage requirements.
NAND flash can support multiple write cycles per block. It offers fast read access but is not as fast as static read-only memory (ROM) or random access memory (RAM). The technology is highly durable and can withstand high and low temperatures and water immersion, making it perform better than hard drives in mobile devices.
NAND flash memory types
The different types of NAND flash memory – SLC, MLC, TLC, QLC, and 3D NAND – essentially refer to how many bits of data can be stored in each cell of the flash memory:
- Single-Level Cell (SLC): This type of NAND flash memory stores one bit of data in each cell, making it the simplest form of NAND. It offers the highest endurance, fastest write speeds, and most extended lifespan but is also the most expensive. SLC NAND is typically used in industrial and enterprise environments where performance and reliability are critical.
- Multi-Level Cell (MLC): MLC stores two data bits in each cell. This results in a lower cost per bit and increases the chip’s capacity but at the expense of lower data write speeds and a reduced lifespan. Due to its balanced performance-to-cost ratio, it is often used in consumer-grade products and some enterprise storage applications.
- Triple-Level Cell (TLC): TLC stores three bits of data per cell, increasing the capacity and reducing the cost per bit. However, this comes at the expense of even lower write performance and endurance. TLC is typically found in consumer-grade products, offering a cost-effective solution for casual use.
- Quad-Level Cell (QLC): QLC stores four bits per cell, making it the highest capacity and cheapest NAND flash. Yet, it has the slowest write performance, the lowest endurance, and a shorter lifespan. It is mainly used for high-capacity, read-intensive scenarios like cold storage.
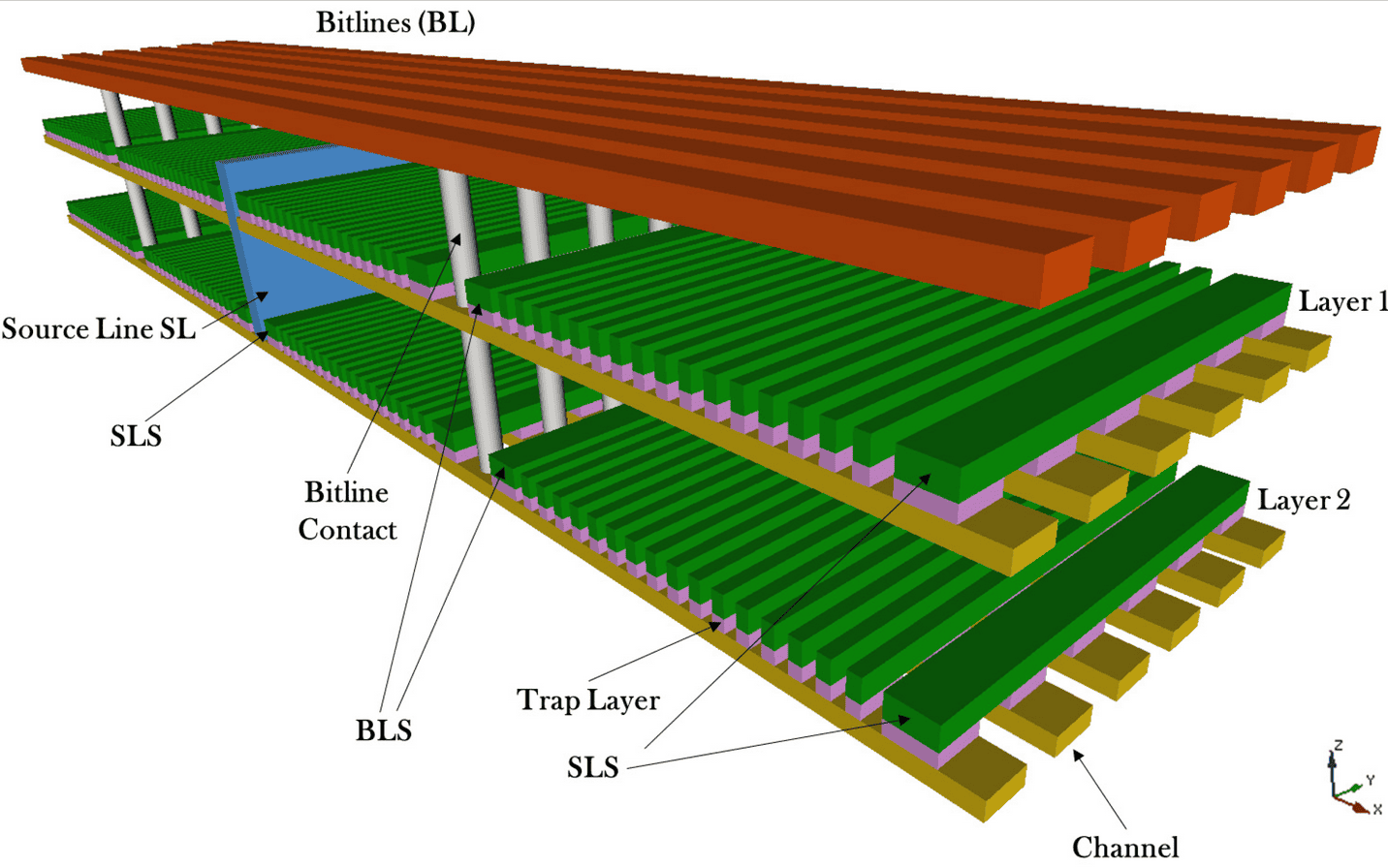
- 3D NAND: Also known as Vertical NAND (V-NAND), 3D NAND is a type of flash memory in which the memory cells are stacked vertically in multiple layers. It was developed to address the scaling problem in planar (2D) NAND technology, achieving higher densities and lower costs per bit. Stacking cells vertically makes it possible to fit more cells in the same amount of physical space, significantly increasing storage capacity. Samsung, for instance, has managed to stack as many as 100 layers in a single die.
As for the terms “raw” and “managed” NAND, these refer to whether or not the NAND requires external memory management:
- Raw NAND: This is the most basic form of NAND flash, and it requires additional error correction and management functions to maintain data integrity. These functions can be handled by a separate controller chip or integrated into the device’s central processor. Raw NAND flash is typically used in high-cost devices, and the software and hardware can handle the extra management functions.
- Managed NAND: This type of NAND includes built-in memory management functions such as error correction code (ECC), wear leveling, and bad block management, which simplify system design and extend the life of the device. Managed NAND devices are often used in high-performance applications where reliability and data integrity are crucial.
NAND vs. NOR flash
Yes, NAND and NOR flash memory differ in purpose, architecture, and characteristics, which has implications for how and where they are used.
Here’s a detailed explanation of the differences:
- Usage:
- NAND Flash Memory: It’s mainly used for storing data, much like a hard drive or SSD in a computer. It offers high storage capacity and write and erase speeds, making it ideal for storing files, operating system data, etc.
- NOR Flash Memory: It’s often used to store and execute code, much like the RAM or ROM in a computer. It allows full address and data buses to read and write to any address, making it ideal for firmware or application code storage.
- Read/Write Speed:
- NAND Flash Memory: It has faster write, read, and erase times than NOR Flash. However, it requires an entire block to be written or erased at once, which can slow down operations if you only need to modify a small amount of data.
- NOR Flash Memory: It offers slower write, read, and erase times than NAND Flash. However, it can read, write, or erase any byte of memory independently, which can be advantageous when code needs to be executed directly from memory.
- Density and Cost:
- NAND Flash Memory: It’s less expensive per bit and offers a higher density, meaning you can store more data in the same amount of physical space. This makes NAND ideal for high-capacity data storage.
- NOR Flash Memory: It’s more expensive per bit and offers a lower density. However, its ability to execute code directly from memory suits specific applications, like storing a device’s firmware.
- Endurance:
- NAND Flash Memory: NAND flash generally offers higher endurance than NOR flash, which can withstand more write/erase cycles. This makes it suitable for applications that require frequent data updates.
- NOR Flash Memory: NOR Flash has lower endurance than NAND Flash. However, since it’s often used for storing firmware that rarely needs updating, this lower endurance is less of an issue.
- Architecture:
- NAND Flash Memory: NAND uses a series architecture that connects the memory cells in a way that resembles a NAND gate. It’s arranged in blocks, which are grouped into pages. Pages and blocks are the reading, writing, and erasing operations units.
- NOR Flash Memory: NOR uses a parallel architecture where cells are connected in parallel to the bit lines, allowing cells to be read and written individually. This architecture resembles a NOR gate, hence the name.
In conclusion, NAND and NOR flash memories serve different purposes and are optimized for those purposes through their architecture, cost, and performance characteristics. Due to their architecture, they’re named for the logic gate they resemble. Choosing between NAND and NOR flash memory involves considering factors like the need for data storage versus code execution, cost considerations, and the required write/erase speeds and endurance.
What is NAND Flash used for?
Here are some detailed examples of its uses:
- Solid State Drives (SSDs): NAND flash memory is a crucial component in SSDs, which are found in computers, servers, and many other devices. Compared to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs), SSDs with NAND flash memory offer higher speed, lower power consumption, and improved reliability. They are also more resistant to physical shocks and have faster access times because they have no moving parts.
- USB Flash Drives and SD Cards: These portable storage devices use NAND flash memory due to their nonvolatile nature and high storage density. It can retain stored information even when power is disconnected, making it ideal for transferring files between devices.
- Smartphones and Tablets: NAND flash memory is used extensively in smartphones and tablets for data storage. It stores the operating system, applications, and user data, such as photos, videos, and music.
- Embedded Systems: Many embedded systems, such as those in automotive applications, industrial control systems, and home automation devices, use NAND flash memory for storing firmware and operating system code. These systems often require reliable, fast, and durable memory solutions, and NAND Flash fits these needs.
- Digital Signage and Advertising Boards: NAND flash memory can store and display dynamic digital content in these applications. Its high storage density and durability make it ideal for outdoor use, where the system needs to operate reliably in various weather conditions.
- AI and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning models often need to process large amounts of data. NAND flash-based SSDs can provide the high-speed, high-capacity storage that these systems require.
Different grades of NAND flash memory, such as industrial-grade and consumer-grade, offer different performance, reliability, and endurance characteristics. Industrial-grade NAND flash is designed for applications requiring high reliability and endurance, such as automotive or aviation electronics. In contrast, consumer-grade NAND flash is used in applications where cost is a primary consideration, such as consumer electronics.
As one of the leading manufacturers of NAND flash memory, Micron offers a wide range of products suitable for various applications, from mobile devices to data center storage solutions. By continuously innovating and improving its design and manufacturing processes, Micron strives to solve design challenges and meet the evolving demands of the market.
The increase in NAND flash prices since 2007 can be attributed to several factors, including the increasing demand for high-capacity storage in various sectors, the transition from 2D to 3D NAND technology, which required substantial investment in new manufacturing processes, and periodic supply-demand imbalances in the semiconductor industry.
Conclusion
NAND flash memory is a critical technology that has become ubiquitous in the digital world. It’s a type of nonvolatile storage that retains data even when power is not supplied, making it ideal for many applications.
Its primary uses span various devices and systems, including, but not limited to, Solid-State Drives (SSDs), USB flash drives, SD cards, smartphones, tablets, and embedded systems. Moreover, due to its capacity, speed, and durability, it’s extensively utilized in more advanced applications such as AI, machine learning, and industrial control systems.
Different types of NAND flash memory, namely SLC, MLC, TLC, QLC, and 3D NAND, are designed with varying numbers of bits per cell, which directly impact their performance, endurance, and cost. SLC, the most durable and reliable, is generally more expensive and used in high-performance industrial applications. On the other end of the spectrum, QLC, with its high storage density and cost-effectiveness, is suitable for high-capacity, read-intensive storage.
NAND flash memory comes in consumer and industrial grades, addressing reliability, endurance, and cost needs. Due to cost considerations, consumer-grade NAND is used extensively in personal electronics, while industrial-grade NAND is utilized in sectors that require high reliability and durability, like automotive or aviation electronics.