In modern digital technologies, “Big Data” has surfaced as a pivotal element for businesses and researchers. Its emergence stems from the need to understand and leverage the explosion of digital data created and consumed by a rapidly growing digital population. The three Vs. of Big Data—volume, Velocity, and Variety—epitomize its core characteristics and challenges. This article delves into these three Vs intricate worlds, explaining their significance, potential complications, and strategies to manage and utilize them effectively.
The Concept of Big Data
Before diving into the three Vs. of Big Data, comprehending the term “Big Data.” Big Data refers to the massive amount of information generated across various digital platforms in structured, semi-structured, or unstructured forms. The data could emanate from multiple sources, including social media, online transactions, sensors, machines, satellites, etc. The enormity of this data, alongside its valuable insights, makes managing, analyzing, and interpreting it both challenging and crucial for businesses, governments, and organizations worldwide.
What Are the 3 Vs of Big Data?
The 3Vs or Three Vs. of Big Data are volumes, Variety, and Velocity. These characteristics are used to describe different aspects of big data. Volume represents the amount of data, Variety represents the number of data types, and Velocity represents data processing speed.
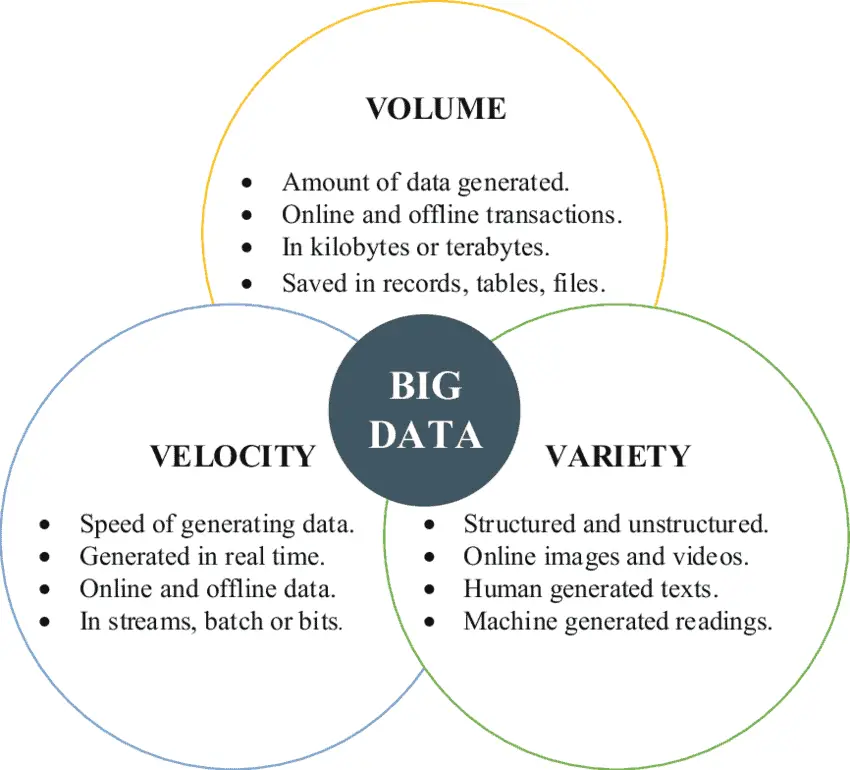
As indicated by the 3Vs model, the difficulties of ample information for executives result from developing every one of the three properties instead of simply the volume alone—the sheer measure of information to be overseen. An association can be better equipped to manage extensive information challenges by understanding the 3Vs of the enormous information on the board.
In literature, we can see other terms as well.
What Are the 5 Vs of Big Data?
The Five Vs of Big Data are volumes, Variety, Velocity, integrity, and value. Volume represents the amount of data, Variety represents the number of data types, Velocity represents data processing speed, and veracity means data quality and values the ability to transform big data into business.
What Are the 7 Vs of Big Data?
The 7 Vs. or Seven Vs. of Big Data are volumes, Variety, Velocity, veracity, value, variability, and visualization. Volume represents the amount of data; Variety represents the number of data types; Velocity represents data processing speed; veracity means the quality of data; variability means constantly changing data; visualization is using charts and graphs to visualize large amounts of data; and value ability to transform big data into business.
Take, for instance, the label group of “cloud” and “enormous information.” The expression “cloud” came about because of frameworks engineers used to draw network graphs of neighborhoods. Between the graphs of LANs, we’d draw a cloud-like tangle intended to allude to “the vague stuff in the middle.” obviously, the Internet turned into definitive unclear stuff in the middle, and the cloud turned into The Cloud.
Volume: The Massiveness of Data
The first V, Volume, refers to the sheer quantity of data generated. With the world’s data predicted to reach a whopping 175 zettabytes by 2025, the enormity of data in existence today is almost unfathomable. This voluminous data growth stems from the proliferation of the Internet of Things (IoT), the surge of social media, increased online transactions, and the rise of machine-generated data.
Dealing with this vast volume of data presents a challenge. Traditional data management tools often fall short when faced with such quantities, necessitating the development of new storage, processing, and analysis technologies. Solutions like distributed storage systems (like Hadoop) and cloud-based platforms have emerged to address these challenges, allowing organizations to store and process colossal data volumes efficiently.
The potential of high-volume data extends beyond its challenges. When analyzed correctly, this data can offer rich insights, helping businesses understand customer behavior, predict market trends, make informed decisions, and create targeted marketing strategies.
Velocity: The Speed of Data Generation and Processing
Velocity, the second V, describes the speed at which data is created, processed, and analyzed. As technology evolves, data is generated at an unprecedented rate. Every minute, users worldwide send hundreds of millions of emails, conduct millions of searches, and generate vast amounts of data through digital interactions.
The challenge with Velocity is not just about how quickly data is produced but also how rapidly it must be processed to extract valuable insights. In some scenarios, real-time or near-real-time information processing can be critical. For instance, financial institutions must detect fraudulent transactions immediately, and healthcare monitors require real-time patient data to provide accurate readings.
Stream processing technologies like Apache Kafka and Spark Streaming have emerged to handle high-speed data. These systems can process and analyze data in real-time, enabling businesses to make instant decisions. Additionally, edge computing has gained traction, wherein computations are performed closer to the data source, reducing latency and enabling faster data processing.
Variety: The Diversity of Data
The third V, Variety, pertains to the different data types available. Data can come in numerous formats – structured data like databases, semi-structured data like XML files, or unstructured data like text documents, videos, and images. The rise of IoT devices and social media has led to an explosion of unstructured and semi-structured data, adding another complexity to data management and analysis.
The challenge lies in integrating these varied data forms into a coherent whole for analysis. Traditional data analysis tools often struggle with unstructured and semi-structured data, leading to more robust solutions like NoSQL databases and natural language processing algorithms.
Despite its challenges, data variety offers many opportunities. Diverse data sources provide a more comprehensive view of the situation or problem, leading to more accurate analyses and predictions. For instance, analyzing social media posts (unstructured data) alongside purchase histories (structured data) can give businesses a complete understanding of customer behavior.
My practical example of Big data in the E-commerce industry
Let’s examine the field of E-commerce, an industry where the impact of Volume, Velocity, and Variety in Big Data is significantly visible.
E-commerce Industry and Big Data Volume
E-commerce companies like Amazon or Alibaba deal with millions of transactions every day. Every single one of these transactions generates data. This includes customer information, purchase details, time of purchase, method of payment, and much more. Additionally, data is generated from customer reviews, clickstreams, website logs, and third-party sources.
This data’s sheer volume is enormous, fitting the first V of Big Data. E-commerce companies leverage advanced data processing and storage tools to harness this data’s potential. For instance, distributed computing systems like Hadoop enable the storing and processing large data sets across computing clusters. By effectively managing and analyzing these vast volumes of data, companies can uncover buying patterns, customer preferences, and trends, shaping their marketing strategies and offerings accordingly.
E-commerce Industry and Big Data Velocity
In the e-commerce industry, data is not only voluminous but also streams in at high speed. For instance, customer browsing data, clickstreams, transactions, and interactions on the website or app are generated in real-time. The data velocity increases even further during peak shopping seasons or promotional campaigns.
The challenge here lies in promptly capturing, processing, and analyzing this data. Real-time or near-real-time processing can provide valuable insights such as detecting fraudulent transactions, real-time personalization, or dynamic pricing. Technologies like Apache Kafka, a real-time data streaming platform, or Spark Streaming, a real-time data processing tool, handle this high-speed data.
E-commerce Industry and Big Data Variety
E-commerce businesses deal with a wide variety of data. Structured data includes transaction details, customer demographics, and product information. Semi-structured data may come from email marketing responses or XML files, but unstructured data could include customer reviews, social media posts, or images.
Though challenging to integrate and analyze, this Variety of data provides a more comprehensive view of the customer. For example, analyzing customer reviews and social media posts can provide insights into customer sentiment, while structured transaction data can reveal buying patterns. Natural language processing tools can help analyze unstructured text, and NoSQL databases can handle diverse data formats, aiding the integration and analysis process.
The e-commerce industry’s ability to handle the three Vs. of Big Data—volume, Velocity, and Variety—directly impacts its success. By harnessing the power of Big Data, companies can gain in-depth customer insights, personalize customer experiences, streamline operations, and enhance decision-making processes. Consequently, the effective management of Big Data can significantly boost customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and, ultimately, the bottom line.
Conclusion
Understanding the three Vs. of Big Data—volume, Velocity, and Variety—is integral to navigating today’s data-driven world. These Vs. Encapsulate the challenges and opportunities that come with handling Big Data. By effectively managing these aspects, businesses and organizations can unlock the full potential of Big Data, converting raw, chaotic information into actionable insights.
Advancements in technology continue to provide solutions for these challenges, with new tools and strategies continually developed to handle the vast volumes, high Velocity, and diverse data. By leveraging these technologies, organizations can harness the power of Big Data to drive decision-making, inform strategy, and ultimately gain a competitive edge in their respective sectors.
- Facebook Ads to Get Followers! - December 27, 2024
- ClickUp vs. Slack - December 20, 2024
- Mastering E-Commerce Analytics: A Blueprint for Success